Business inventories uses cpi for smarter economic planning is rapidly becoming a focal point in today’s fast-paced financial landscape, changing the way companies and policymakers interpret and act on economic signals. Dive into this fascinating world where tracking goods on shelves meets the pulse of inflation, unlocking insights that drive strategic decisions for businesses of all sizes.
At its core, business inventories refer to the goods and materials that companies keep on hand, while the Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures the average change in prices paid by consumers over time. The relationship between the two is crucial, as shifts in inventory levels can impact how inflation is measured and understood. Keeping a close eye on both allows businesses and governments to make informed choices about pricing, forecasting, and supply chain management, making these metrics essential tools in economic planning.
Business Inventories and the Consumer Price Index (CPI): Concepts and Interconnections
Business inventories play a crucial role in the economic landscape, serving as a barometer for both operational efficiency and broader market conditions. The Consumer Price Index (CPI), on the other hand, is a widely recognized indicator that measures changes in the average prices paid by consumers for goods and services over time. Understanding how these two metrics interact helps businesses, policymakers, and analysts make sense of inflation and the overall health of the economy.
Definitions and Economic Roles

Business inventories represent the total stock of goods that companies hold for the purpose of resale or production. This includes raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished products. The CPI calculates the average change in prices over time for a fixed basket of goods and services, reflecting the cost of living and purchasing power.
The relationship between business inventories and the CPI is foundational for inflation measurement. Shifts in inventory levels can signal changes in supply and demand, which in turn influence price levels. Accurate inventory tracking is essential, as it feeds into national economic data, helping economists identify trends such as production bottlenecks or emerging inflationary pressures.
Methods Used to Calculate and Value Business Inventories
Tracking and valuing inventories require systematic approaches to ensure accuracy in financial reporting and economic analysis. Businesses commonly use a range of inventory accounting methods, each with unique implications for reported values and profitability.
Common Inventory Accounting Procedures
Routine inventory tracking involves periodic physical counts, automated inventory management systems, and reconciliation with financial records. The chosen valuation method affects reported costs, tax obligations, and even CPI calculations. Here’s a comparison of popular inventory accounting methods:
| Method | Description | Inventory Valuation Impact | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIFO (First-In, First-Out) | Assumes earliest goods purchased are sold first. | In periods of inflation, results in lower cost of goods sold and higher ending inventory value. | Grocery stores needing to rotate perishable stock. |
| LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) | Assumes latest goods purchased are sold first. | In inflationary times, increases cost of goods sold, reducing taxable income. | Industrial suppliers with stable, non-perishable inventory. |
| Weighted Average | Calculates cost based on average of all inventory items. | Smooths out price fluctuations over accounting periods. | Retailers with high-volume, interchangeable goods. |
| Specific Identification | Tracks the actual cost of each individual item sold. | Provides precise inventory valuation, especially for unique or high-value items. | Jewelry or luxury automobile dealerships. |
Selecting the right method depends on business needs, regulatory requirements, and industry practices. Each approach can lead to notably different inventory values on financial statements, which in turn affects economic data and CPI-related analyses.
The Importance of CPI in Economic Decision-Making
CPI is foundational for assessing inflation and guiding a range of economic decisions. It functions as a benchmark for cost-of-living adjustments, wage negotiations, and social security payments.
Benchmark Role and Data Utilization, Business inventories uses cpi
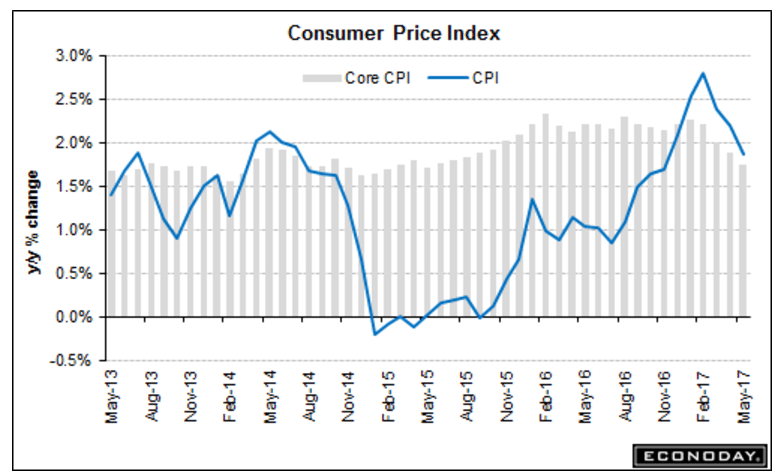
Governments rely on CPI data to set monetary policy, adjust tax brackets, and allocate resources. Businesses use CPI to inform pricing strategies, manage contracts with indexed terms, and anticipate shifts in consumer demand.
In 2023, a major retail chain adjusted its product pricing and purchasing strategies after a sustained rise in CPI signaled an impending increase in supplier costs. By monitoring the index closely, the company managed to maintain profit margins despite inflationary pressures, illustrating the real-world impact of CPI on inventory management.
Integration in Business and Government Planning
CPI data is a key input for budget forecasts, investment analyses, and risk management. In volatile markets, adjusting inventory procurement based on CPI trends can help companies avoid overstocking during high inflation or shortages during price drops.
Influences of Business Inventories on CPI Calculations
Inventory changes directly affect calculated price levels, influencing how inflation is perceived and managed.
Inventory Fluctuations and Price Levels
Understanding the mechanisms by which inventories affect CPI is vital for accurate economic modeling. When inventories rise, it often signals that supply outpaces demand, which can exert downward pressure on prices. Conversely, dwindling inventories may indicate rising demand or supply chain issues, driving prices up.
- Rapid inventory depletion can lead to product shortages and price spikes, pushing CPI higher.
- Surplus inventories can trigger discounts and promotions, moderating overall price levels.
- Delayed or inaccurate inventory reporting may distort CPI readings, misleading policymakers.
- Strategic inventory buildup ahead of anticipated demand surges can smooth out price volatility.
For example, if a major electronics distributor underreports inventory and replenishment lags are not captured in official data, the temporary scarcity may be overstated in CPI figures, leading to incorrect conclusions about inflationary trends.
Closing Summary
In summary, understanding business inventories uses cpi not only clarifies how businesses and governments make vital economic choices but also highlights the importance of accurate data in a dynamic marketplace. With new technologies and refined methods on the horizon, integrating inventory tracking with inflation measurement promises even greater precision, helping decision-makers stay ahead of the curve and respond swiftly to changing economic conditions.
General Inquiries: Business Inventories Uses Cpi
How does business inventory data influence CPI calculation?
Inventory data can affect CPI when changes in stock levels impact supply and demand, which in turn influences retail prices and the calculation of inflation.
Why do businesses need to align inventory tracking with CPI data?
Aligning inventory tracking with CPI helps businesses forecast costs, set competitive prices, and plan for inflationary pressures more accurately.
Can delayed inventory reporting lead to inaccurate CPI readings?
Yes, delays or inaccuracies in inventory reporting can distort the CPI, making inflation appear higher or lower than it really is, which can mislead economic decision-making.
Which industries benefit the most from using both inventory and CPI data?
Retail, manufacturing, and wholesale industries rely heavily on both data sets to manage supply chains, set prices, and forecast demand.
What technological tools improve the integration of inventories and CPI?
Advanced inventory management systems, AI-driven forecasting tools, and real-time data analytics platforms all help enhance the accuracy and timeliness of economic analysis using inventories and CPI.
